首页 > 基础知识 > 正文
原创文章,转载请注明出处!
本文链接:http://daiwk.github.io/posts/knowledge-mpi.html
mpi
标签:mpi
1970-01-01
目录
hello world
#include "mpi.h"
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char* argv[])
{
int rank, numproces;
int namelen;
char processor_name[MPI_MAX_PROCESSOR_NAME];
MPI_Init(&argc, &argv);
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &rank);
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &numproces);
MPI_Get_processor_name(processor_name, &namelen);
fprintf(stderr, "hello world! process %d of %d on %s\n", rank, numproces, processor_name);
MPI_Finalize();
return 0;
}
然后
mpic++ hello.cc -o hello.out
mpirun -n 4 hello.out
输出(其中的xxx.xxx就是机器名):
hello world! process 0 of 4 on xxx.xxx
hello world! process 1 of 4 on xxx.xxx
hello world! process 2 of 4 on xxx.xxx
hello world! process 3 of 4 on xxx.xxx
mpi教程
参考https://github.com/wesleykendall/mpitutorial/tree/gh-pages
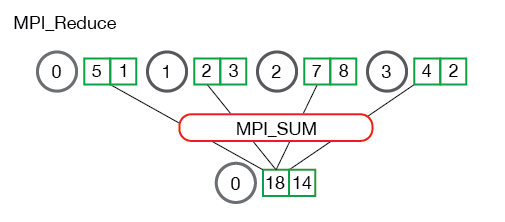
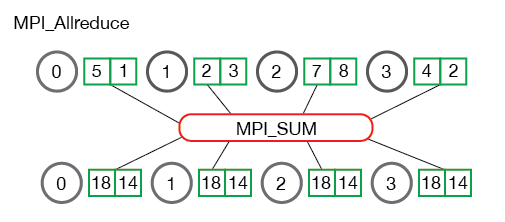
reduce与allreduce
参考http://mpitutorial.com/tutorials/mpi-reduce-and-allreduce/
中文版:https://blog.csdn.net/yiran103/article/details/79851180
先看看makefile
EXECS=reduce_avg reduce_stddev
MPICC?=mpicc
all: ${EXECS}
reduce_avg: reduce_avg.c
${MPICC} -o reduce_avg reduce_avg.c
reduce_stddev: reduce_stddev.c
${MPICC} -o reduce_stddev reduce_stddev.c -lm
clean:
rm -f ${EXECS}
然后reduce的例子是求平均数:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <time.h>
// Creates an array of random numbers. Each number has a value from 0 - 1
float *create_rand_nums(int num_elements) {
float *rand_nums = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * num_elements);
assert(rand_nums != NULL);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_elements; i++) {
rand_nums[i] = (rand() / (float)RAND_MAX);
}
return rand_nums;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: avg num_elements_per_proc\n");
exit(1);
}
int num_elements_per_proc = atoi(argv[1]);
MPI_Init(NULL, NULL);
int world_rank;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_rank);
int world_size;
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_size);
// Create a random array of elements on all processes.
srand(time(NULL)*world_rank); // Seed the random number generator to get different results each time for each processor
float *rand_nums = NULL;
rand_nums = create_rand_nums(num_elements_per_proc);
// Sum the numbers locally
float local_sum = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_elements_per_proc; i++) {
local_sum += rand_nums[i];
}
// Print the random numbers on each process
printf("Local sum for process %d - %f, avg = %f\n",
world_rank, local_sum, local_sum / num_elements_per_proc);
// Reduce all of the local sums into the global sum
float global_sum;
MPI_Reduce(&local_sum, &global_sum, 1, MPI_FLOAT, MPI_SUM, 0,
MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// Print the result
if (world_rank == 0) {
printf("Total sum = %f, avg = %f\n", global_sum,
global_sum / (world_size * num_elements_per_proc));
}
// Clean up
free(rand_nums);
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Finalize();
}
很简单,把所有节点的结果加起来,存到0号节点去

然后求标准差是个allreduce的例子:
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <mpi.h>
#include <math.h>
#include <assert.h>
// Creates an array of random numbers. Each number has a value from 0 - 1
float *create_rand_nums(int num_elements) {
float *rand_nums = (float *)malloc(sizeof(float) * num_elements);
assert(rand_nums != NULL);
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_elements; i++) {
rand_nums[i] = (rand() / (float)RAND_MAX);
}
return rand_nums;
}
int main(int argc, char** argv) {
if (argc != 2) {
fprintf(stderr, "Usage: avg num_elements_per_proc\n");
exit(1);
}
int num_elements_per_proc = atoi(argv[1]);
MPI_Init(NULL, NULL);
int world_rank;
MPI_Comm_rank(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_rank);
int world_size;
MPI_Comm_size(MPI_COMM_WORLD, &world_size);
// Create a random array of elements on all processes.
srand(time(NULL)*world_rank); // Seed the random number generator of processes uniquely
float *rand_nums = NULL;
rand_nums = create_rand_nums(num_elements_per_proc);
// Sum the numbers locally
float local_sum = 0;
int i;
for (i = 0; i < num_elements_per_proc; i++) {
local_sum += rand_nums[i];
}
// Reduce all of the local sums into the global sum in order to
// calculate the mean
float global_sum;
MPI_Allreduce(&local_sum, &global_sum, 1, MPI_FLOAT, MPI_SUM,
MPI_COMM_WORLD);
float mean = global_sum / (num_elements_per_proc * world_size);
// Compute the local sum of the squared differences from the mean
float local_sq_diff = 0;
for (i = 0; i < num_elements_per_proc; i++) {
local_sq_diff += (rand_nums[i] - mean) * (rand_nums[i] - mean);
}
// Reduce the global sum of the squared differences to the root process
// and print off the answer
float global_sq_diff;
MPI_Reduce(&local_sq_diff, &global_sq_diff, 1, MPI_FLOAT, MPI_SUM, 0,
MPI_COMM_WORLD);
// The standard deviation is the square root of the mean of the squared
// differences.
if (world_rank == 0) {
float stddev = sqrt(global_sq_diff /
(num_elements_per_proc * world_size));
printf("Mean - %f, Standard deviation = %f\n", mean, stddev);
}
// Clean up
free(rand_nums);
MPI_Barrier(MPI_COMM_WORLD);
MPI_Finalize();
}
和reduce的区别在于,把所有节点的结果加起来之后,又重新分发到每一个节点啦(相当于Bcast):

原创文章,转载请注明出处!
本文链接:http://daiwk.github.io/posts/knowledge-mpi.html
comment here..