fastai
标签:fast.ai, fastai目录
原文:https://blog.floydhub.com/ten-techniques-from-fast-ai/
安装直接(目前这个版本要求torch<0.4,而autokeras要求>=0.4.0,会有点小diff咯)
pip install fastai
使用多个而不是单一学习率
差分学习率(Differential Learning rates)意味着在训练时变换网络层比提高网络深度更重要。
参考https://github.com/fastai/fastai/blob/master/courses/dl1/lesson1-vgg.ipynb
例如:
from fastai.imports import *
from fastai.transforms import *
from fastai.conv_learner import *
from fastai.model import *
from fastai.dataset import *
from fastai.sgdr import *
from fastai.plots import *
# import library for creating learning object for convolutional #networks
sz=224
arch=vgg16
# assign model to resnet, vgg, or even your own custom model
PATH = './imgs' ##文件夹要是imgs/train/1/xx.jpg, images/valid/1/xx.jpg
data = ImageClassifierData.from_paths(PATH, tfms=tfms_from_model(arch, sz))
# create fast ai data object, in this method we use from_paths where
# inside PATH each image class is separated into different folders
learn = ConvLearner.pretrained(arch, data, precompute=True)
# create a learn object to quickly utilise state of the art
# techniques from the fast ai library
然后,冻结前面网络层并微调后面网络层:
learn.freeze()
# freeze layers up to the last one, so weights will not be updated.
learning_rate = 0.1
learn.fit(learning_rate, epochs=3)
# train only the last layer for a few epochs
当后面的网络效果比较好的时候,可以用差分学习率来改变前面的网络层,实践中,一般将学习率的缩小倍数设置为10倍:
learn.unfreeze()
# set requires_grads to be True for all layers, so they can be updated
learning_rate = [0.001, 0.01, 0.1]
# learning rate is set so that deepest third of layers have a rate of 0.001, # middle layers have a rate of 0.01, and final layers 0.1.
learn.fit(learning_rate, epochs=3)
# train model for three epoch with using differential learning rates
如何找到合适的学习率
一篇周期性学习率的paper:Cyclical Learning Rates for Training Neural Networks
用较低的学习率来训练,但在每个batch中以指数形式增加:
learn.lr_find()
# run on learn object where learning rate is increased exponentially
learn.sched.plot_lr()
# plot graph of learning rate against iterationslr
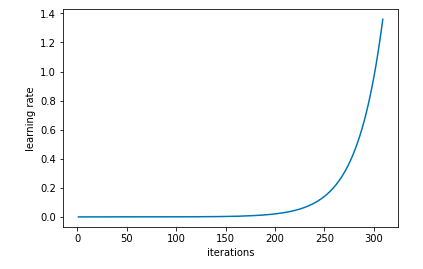
然后可以看看学习率和loss的关系
learn.sched.plot()
# plots the loss against the learning rate
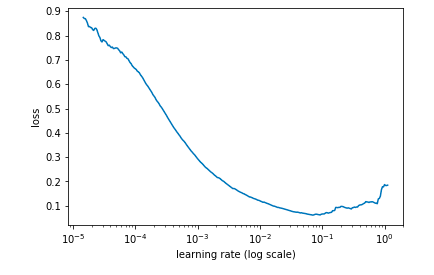
通过找出学习率最高且Loss值仍在下降的值来确定最佳学习率。在上述情况中,该值将为0.01。
cosine annealing
当逐渐接近loss最小值时,学习率应该变得更小来使得模型不会超调且尽可能接近这一点。余弦退火(Cosine annealing)利用余弦函数来降低学习率。
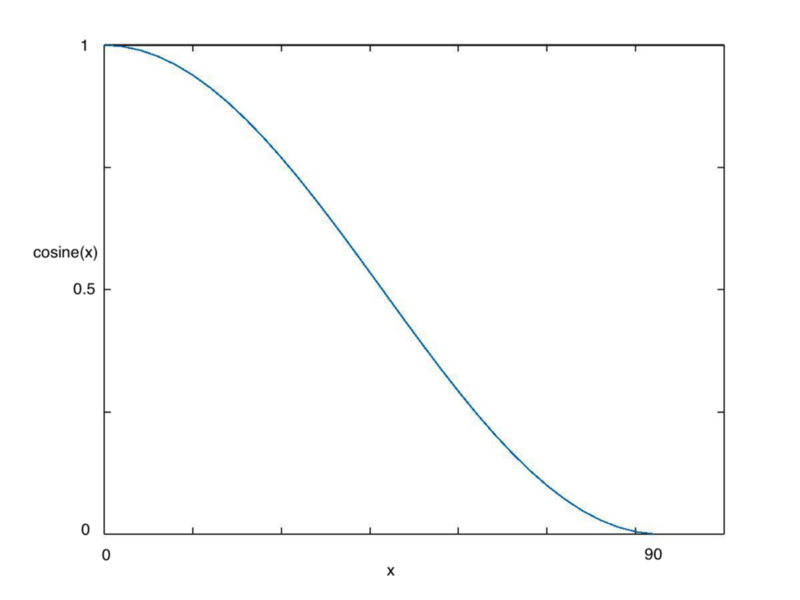
从上图可以看出,随着x的增加,余弦值首先缓慢下降,然后加速下降,再次缓慢下降。
learn.fit(0.1, 1)
# Calling learn fit automatically takes advantage of cosine annealing
Fast.ai库中的learn.fit()函数,来快速实现这个算法,在整个周期中不断降低学习率,如下图所示:
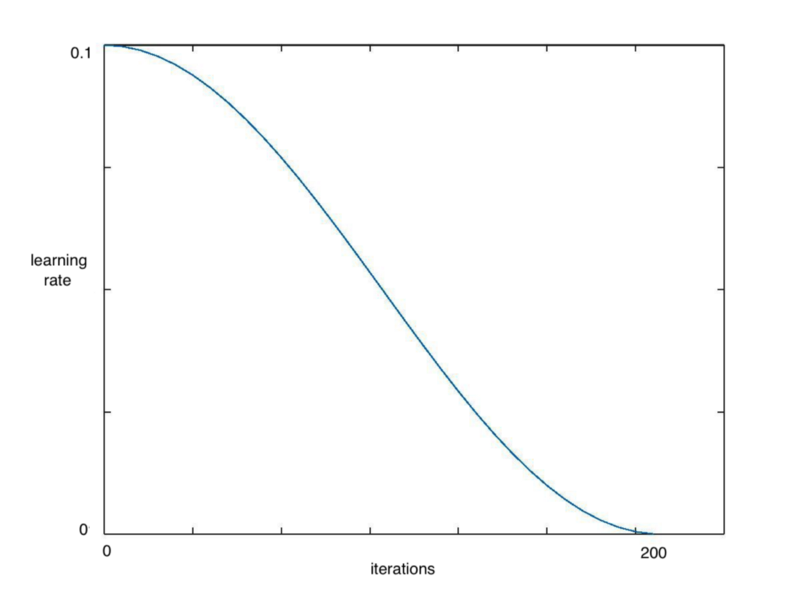
带重启的SGD算法
梯度下降算法可能陷入局部最小值,而不是全局最小值。
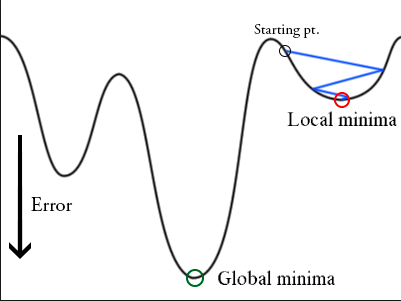
可以通过突然提高学习率,来跳出局部最小值并找到通向全局最小值的路径。这种方式称为带重启的随机梯度下降方法(stochastic gradient descent with restarts, SGDR),这个方法在Loshchilov和Hutter的ICLR论文中展示出了很好的效果。SGDR: Stochastic Gradient Descent with Warm Restarts
当调用learn.fit(learning_rate, epochs)函数时,学习率在每个周期开始时重置为参数输入时的初始值,然后像上面余弦退火部分描述的那样,逐渐减小。
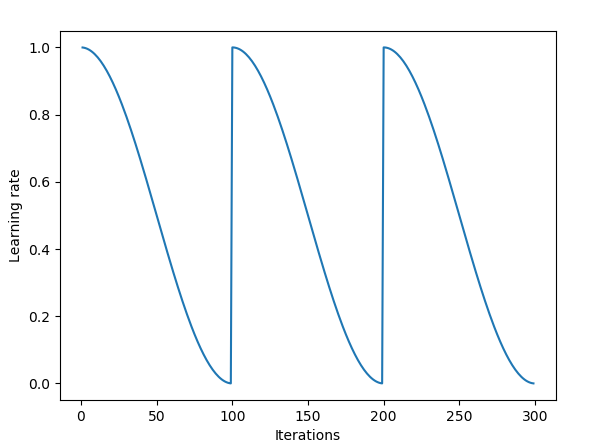
每当学习率下降到最小点,在上图中为每100次迭代,我们称为一个循环。
cycle_len = 1
# decide how many epochs it takes for the learning rate to fall to
# its minimum point. In this case, 1 epoch
cycle_mult=2
# at the end of each cycle, multiply the cycle_len value by 2
learn.fit(0.1, 3, cycle_len=2, cycle_mult=2)
# in this case there will be three restarts. The first time with
# cycle_len of 1, so it will take 1 epoch to complete the cycle.
# cycle_mult=2 so the next cycle with have a length of two epochs,
# and the next four.
如果我们把cycle_mult设成2:
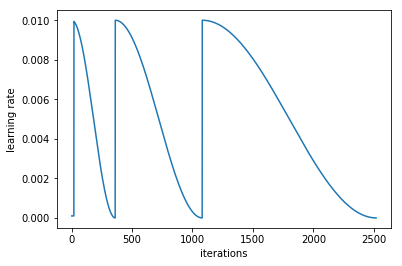
关于这两个cycle_mult和cycle_len的函数,可以参考http://forums.fast.ai/t/understanding-cycle-len-and-cycle-mult/9413/8
原创文章,转载请注明出处!
本文链接:http://daiwk.github.io/posts/platform-fastai.html