tensorflow代码解析——概览
标签:tensorflow代码, 代码解析, 概览目录
参考:
- 强行置顶!!!!https://github.com/horance-liu/tensorflow-internals
- A tour through the TensorFlow codebase
- 『深度长文』Tensorflow代码解析(一)
- 『深度长文』Tensorflow代码解析(二)
- 『深度长文』Tensorflow代码解析(三)
- 『深度长文』Tensorflow代码解析(四)
- 『深度长文』Tensorflow代码解析(五)
简介
总体结构
从底向上分为设备管理和通信层、数据操作层、图计算层、API接口层、应用层。
- 底层设备通信层负责网络通信和设备管理。
- 设备管理可以实现TF设备异构的特性,支持CPU、GPU、Mobile等不同设备。
- 网络通信依赖gRPC通信协议实现不同设备间的数据传输和更新。
- 数据操作层是Tensor的OpKernels实现。这些OpKernels以Tensor为处理对象,依赖网络通信和设备内存分配,实现了各种Tensor操作或计算。Opkernels不仅包含MatMul等计算操作,还包含Queue等非计算操作
- 图计算层(Graph),包含本地计算流图和分布式计算流图的实现。Graph模块包含Graph的创建、编译、优化和执行等部分,Graph中每个节点都是OpKernels类型表示。
- API接口层。Tensor C API是对TF功能模块的接口封装,便于其他语言平台调用。
- 应用层。不同编程语言在应用层通过API接口层调用TF核心功能实现相关实验和应用。
代码结构
以2018.09.23的master为基准:
tensorflow/core
其中,tensorflow/core目录包含了TF核心模块代码:
public: API接口头文件目录,用于外部接口调用的API定义,主要是session.h。client: API接口实现文件目录。(目前已经没有这个目录了…)platform:OS系统相关接口文件,如file system, env等。protobuf: 均为.proto文件,用于数据传输时的结构序列化。(都是proto3的语法)common_runtime: 公共运行库,包含session,executor,threadpool,rendezvous,memory管理,设备分配算法等。distributed_runtime: 分布式执行模块,如rpc session,rpc master,rpc worker,graph manager。framework: 包含基础功能模块,如log,memory,tensorgraph: 计算流图相关操作,如construct,partition,optimize,execute等kernels: 核心Op,如matmul,conv2d,argmax,batch_norm等lib: 公共基础库,如gif、gtl(google模板库)、hash、histogram、jpeg、png、wav等。ops: 基本ops运算(xxx_ops.cc),ops梯度运算(xxx_grad.cc),io相关的ops(io_ops.cc),控制流和数据流*操作(control_flow_ops.cc和data_flow_ops.cc)
tensorflow/stream_executor
tensorflow/stream_executor目录是并行计算框架,由google stream executor团队开发。
tensorflow/contrib
tensorflow/contrib目录是contributor开发目录。
tensroflow/python
tensroflow/python目录是python API客户端脚本
third_party
- eigen3:eigen矩阵运算库,tf基础ops调用
- gpus: 封装了cuda/cudnn编程库
tf核心概念
tf的核心是围绕Graph展开的,简而言之,就是Tensor沿着Graph传递闭包完成Flow的过程。
Tensor
Matrix表示二维线性映射,Tensor表示多维线性映射。TF中Tensor的维数描述为阶,数值是0阶,向量是1阶,矩阵是2阶,以此类推,可以表示n阶高维数据。
tensor contraction
matrix的product和tensor的contract运算如下:
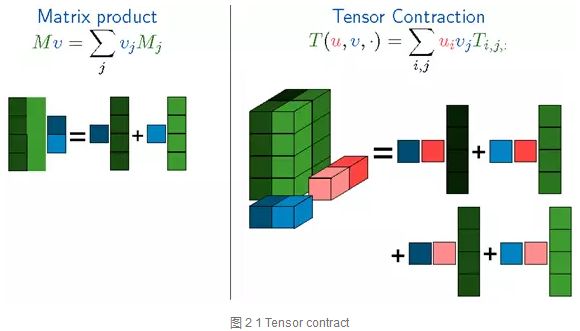
可见,一个4x2的A与一个2x1的B矩阵相乘,可以变成两个矩阵相加,每一个是一个1x1与一个4x1相乘,就是A矩阵的两列分别与B的两列分别相乘,再相加
contract是tensor的运算,python实现可以看:tensorflow/tensorflow/python/ops/math_ops.py,即tensordot(也称为张量收缩)对从a和b所指定的索引a_axes和b_axes的元素的乘积进行求和。a_axes和b_axes是两个数组,指定沿其收缩张量的那些轴对。对于所有range(0, len(a_axes))中的i,a的轴a_axes[i]必须与b的轴b_axes[i]具有相同的维度。列表a_axes和b_axes必须具有相同的长度,并由唯一的整数组成,用于为每个张量指定有效的坐标轴。
该操作对应于numpy.tensordot(a, b, axes),numpy.tensordot文档。
- 示例1:当a和b是矩阵(2阶)时,
axes = 1相当于矩阵乘法。 - 示例2:当a和b是矩阵(2阶)时,
axes = [[1], [0]]相当于矩阵乘法。 - 示例3:假设
\(a_ {ijk}\)和\(b_ {lmn}\)表示3阶的两个张量。那么,contract(a, b, [[0], [2]])是4阶张量\(c_ {jklm}\),其条目对应于索引\((j,k,l,m)\)由下式给出:
\[
c_{jklm} = \sum_i a_{ijk} b_{lmi}
\]
可见,因为传入的是[[0],[2]],所以ijk的第0维,即i,和lmn的第2维,即n,都变成了i,然后求和~
一般来说,order(c) = order(a) + order(b) - 2*len(axes[0])。
Tensor实现
Tensor在高维空间数学运算比Matrix计算复杂,计算量也非常大,加速张量并行运算是TF优先考虑的问题,如add, contract, slice, reshape, reduce, shuffle等运算。
TF中Tensor支持的数据类型有很多,如tf.float16, tf.float32, tf.float64, tf.uint8, tf.int8, tf.int16, tf.int32, tf.int64, tf.string, tf.bool, tf.complex64等,所有Tensor运算都使用*泛化的数据类型`*(可以重载*和+运算咯)表示。
Tensor定义和运算主要是调用Eigen矩阵计算库完成的。
Tensor的定义在tensorflow/core/framework/tensor.h中。
Tensor的两个主要的成员变量
TensorShape shape_;
TensorBuffer* buf_;
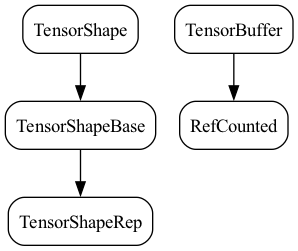
TensorShape在tensorflow/core/framework/tensor_shape.h中定义,基类是TensorShapeBase:
class TensorShape : public TensorShapeBase<TensorShape>
TensorShapeBase如下:
/// Represents the shape of a Tensor.
///
/// A tensor's shape is denoted by its number of dimensions and a size for each
/// dimension. For example, a Tensor represented by a 3 x 4 matrix would have
/// a shape of 2-D, [3,4].
///
/// If you know the exact shape of your Tensor when you create the TensorShape
/// object, you can specify it then, or you can create a TensorShape with
/// zero dimensions and one element, and call AddDim() to add dimensions later.
class TensorShape : public TensorShapeBase<TensorShape> {
public:
using TensorShapeBase<TensorShape>::TensorShapeBase;
/// Allow a TensorShape to be used as a PartialTensorShape without copying
operator const PartialTensorShape&() const; // NOLINT(runtime/explicit)
/// Returns true if `*this` and `b` have the same sizes. Ignores
/// dimension names.
bool IsSameSize(const TensorShape& b) const;
bool operator==(const TensorShape& b) const { return IsSameSize(b); }
bool operator!=(const TensorShape& b) const { return !IsSameSize(b); }
/// Fill `*dsizes` from `*this`.
template <int NDIMS>
Eigen::DSizes<Eigen::DenseIndex, NDIMS> AsEigenDSizes() const;
/// Same as `AsEigenDSizes()` but allows for `NDIMS > dims()` -- in
/// which case we pad the rest of the sizes with 1.
template <int NDIMS>
Eigen::DSizes<Eigen::DenseIndex, NDIMS> AsEigenDSizesWithPadding() const;
private:
// These CHECK fail to ease debugging.
// REQUIRES: dims() == NDIMS
void CheckDimsEqual(int NDIMS) const;
// REQUIRES: dims() >= NDIMS
void CheckDimsAtLeast(int NDIMS) const;
};
其中,TensorShapeBase是TensorShapeRep的子类
/// Base class for TensorShape and PartialTensorShape.
/// The class is templatized by either TensorShape or PartialTensorShape to
/// allow skipping known/unknown checks in the TensorShape case, but the
/// representation is shared exactly for fast conversion.
template <class Shape>
class TensorShapeBase : public TensorShapeRep
TensorBuffer是tensorflow/core/lib/core/refcount.h的RefCounted(引用计数器)的子类
class TensorBuffer : public core::RefCounted
Tensor的主要函数
返回Eigen::Tensor类型的主要函数:
template <typename T>
typename TTypes<T>::Vec vec() {
return tensor<T, 1>();
}
// 其中,typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>, Eigen::Aligned> Vec;
template <typename T>
typename TTypes<T>::Matrix matrix() {
return tensor<T, 2>();
}
// 其中,typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 2, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>, Eigen::Aligned> Matrix;
template <typename T, size_t NDIMS>
typename TTypes<T, NDIMS>::Tensor tensor();
// 其中,typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, NDIMS, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>, Eigen::Aligned> Tensor;
其中的TTypes定义在tensorflow/core/framework/tensor_types.h中,如下:
// Helper to define Tensor types given that the scalar is of type T.
template <typename T, int NDIMS = 1, typename IndexType = Eigen::DenseIndex>
struct TTypes {
// Rank-<NDIMS> tensor of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, NDIMS, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>,
Eigen::Aligned>
Tensor;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, NDIMS, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>, Eigen::Aligned>
ConstTensor;
// Unaligned Rank-<NDIMS> tensor of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, NDIMS, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedTensor;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, NDIMS, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedConstTensor;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, NDIMS, Eigen::RowMajor, int>,
Eigen::Aligned>
Tensor32Bit;
// Scalar tensor (implemented as a rank-0 tensor) of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::TensorFixedSize<T, Eigen::Sizes<>, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>,
Eigen::Aligned>
Scalar;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::TensorFixedSize<const T, Eigen::Sizes<>,
Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>,
Eigen::Aligned>
ConstScalar;
// Unaligned Scalar tensor of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::TensorFixedSize<T, Eigen::Sizes<>, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedScalar;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::TensorFixedSize<const T, Eigen::Sizes<>,
Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedConstScalar;
// Rank-1 tensor (vector) of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>,
Eigen::Aligned>
Flat;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>, Eigen::Aligned>
ConstFlat;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>,
Eigen::Aligned>
Vec;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>, Eigen::Aligned>
ConstVec;
// Unaligned Rank-1 tensor (vector) of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedFlat;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedConstFlat;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedVec;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, 1, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedConstVec;
// Rank-2 tensor (matrix) of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 2, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>,
Eigen::Aligned>
Matrix;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, 2, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType>, Eigen::Aligned>
ConstMatrix;
// Unaligned Rank-2 tensor (matrix) of scalar type T.
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<Eigen::Tensor<T, 2, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedMatrix;
typedef Eigen::TensorMap<
Eigen::Tensor<const T, 2, Eigen::RowMajor, IndexType> >
UnalignedConstMatrix;
};
用法如下:
typedef float T;
Tensor my_mat(...built with Shape{rows: 3, cols: 5}...);
auto mat = my_mat.matrix<T>(); // 2D Eigen::Tensor, 3 x 5.
auto mat = my_mat.tensor<T, 2>(); // 2D Eigen::Tensor, 3 x 5.
auto vec = my_mat.vec<T>(); // CHECK fails as my_mat is 2D.
auto vec = my_mat.tensor<T, 3>(); // CHECK fails as my_mat is 2D.
auto mat = my_mat.matrix<int32>();// CHECK fails as type mismatch.
Eigen::Tensor
eigen源码:
https://bitbucket.org/eigen/eigen/src/8dd2d6552a87?at=default
git上的源码:
https://github.com/eigenteam/eigen-git-mirror
Eigen::Tensor不属于Eigen官方维护的程序,由贡献者提供文档和维护,所以Tensor定义在Eigen unsupported模块中(#include "third_party/eigen3/unsupported/Eigen/CXX11/Tensor")
参考http://eigen.tuxfamily.org/dox-devel/unsupported/classEigen_1_1Tensor.html
Tensor主要包含一个变量TensorStorage<Scalar, Dimensions, Options> m_storage,而TensorStorage里有两个变量m_data和m_dimensions,m_data保存了Tensor的数据块,T是泛化的数据类型,m_dimensions保存了Tensor的维度信息。
EIGEN_ALIGN_MAX T m_data[MinSize];
FixedDimensions m_dimensions;
Eigen::Tensor的成员变量很简单,却支持非常多的基本运算,再借助Eigen的加速机制实现快速计算。Eigen::Tensor主要包含了
- 一元运算(Unary),如sqrt、square、exp、abs等。
- 二元运算(Binary),如add,sub,mul,div等
- 选择运算(Selection),即if / else条件运算
- 归纳运算(Reduce),如reduce_sum, reduce_mean等
- 几何运算(Geometry),如reshape,slice,shuffle,chip,reverse,pad,concatenate,extract_patches,extract_image_patches等
- 张量积(Contract)和卷积运算(Convolve)是重点运算,后续会详细讲解。
符号编程
编程模式通常分为命令式编程(imperative style programs)和符号式编程(symbolic style programs)。
- 命令式编程:容易理解和调试,命令语句基本没有优化,按原有逻辑执行。
- 符号式编程:涉及较多的嵌入和优化,不容易理解和调试,但运行速度有同比提升。
命令式编程明确输入变量,并根据程序逻辑逐步运算,这种模式非常在调试程序时进行单步跟踪,分析中间变量。
符号式编程将计算过程抽象为计算图,计算流图可以方便的描述计算过程,所有输入节点、运算节点、输出节点均符号化处理。
和目前的符号语言比起来,TF最大的特点是强化了数据流图,引入了mutation的概念。所谓mutation,就是可以在计算的过程中更改一个变量的值,而这个变量在计算的过程中会被带入到下一轮迭代里面去。mutation是机器学习优化算法几乎必须要引入的东西(虽然也可以通过immutable replacement来代替,但是会有效率的问题),这一点会导致最后的API设计和使用需要特别小心,把mutation引入到数据流图中会带来一些新的问题,比如,如何处理写与写之间的依赖。
梯度计算
梯度计算涉及每个计算节点,每个自定义的前向计算图都包含一个隐式的反向计算图。从数据流向上看,正向计算图是数据从输入节点到输出节点的流向过程,反向计算图是数据从输出节点到输入节点的流向过程。
反向计算限制了符号编程中内存空间复用的优势,因为在正向计算中的计算数据在反向计算中也可能要用到。从这一点上讲,粗粒度的计算节点比细粒度的计算节点更有优势,而TF大部分为细粒度操作,虽然灵活性很强,但细粒度操作涉及到更多的优化方案,在工程实现上开销较大,不及粗粒度简单直接。在神经网络模型中,TF将逐步侧重粗粒度运算。
控制流
TF的计算图如同数据流一样,数据流向表示计算过程。数据流图可以很好的表达计算过程,为了扩展TF的表达能力,TF中引入控制流。编程语言中,if…else…是最常见的逻辑控制,在TF的数据流中也可以通过这种方式控制数据流向。接口函数如下,pred为判别表达式,fn1和fn2为运算表达式。当pred为true是,执行fn1操作;当pred为false时,执行fn2操作。
tf.cond(pred, fn1, fn2, name=None)
TF还可以协调多个数据流,在存在依赖节点的场景下非常有用,例如节点B要读取模型参数\(\theta\)更新后的值,而节点A负责更新参数\(\theta\),则节点B必须等节点A完成后才能执行,否则读取的参数\(\theta\)为更新前的数值,这时需要一个运算控制器。接口函数如下,tf.control_dependencies函数可以控制多个数据流执行完成后才能执行接下来的操作,通常与tf.group函数结合使用。
tf.control_dependencies(control_inputs)
TF支持的控制算子有Switch、Merge、Enter、Leave和NextIteration等。
TF不仅支持逻辑控制,还支持循环控制。TF使用和MIT Token-Tagged machine(即Executing a program on the MIT tagged-token dataflow architecture.)相似的表示系统,将循环的每次迭代标记为一个tag,迭代的执行状态标记为一个frame,但迭代所需的数据准备好的时候,就可以开始计算,从而多个迭代可以同时执行。
原创文章,转载请注明出处!
本文链接:http://daiwk.github.io/posts/platform-tensorflow-code-analysis-overview.html